Spur gears are a significant gear type that is utilized in numerous industrial and mechanical applications. They are a well-liked option for a variety of industries because of their famed simplicity, dependability, and ease of manufacture. We shall discuss spur gears, their composition, advantages and disadvantages, typical uses, and maintenance and repair issues in this article.
Anatomy of a Spur Gear
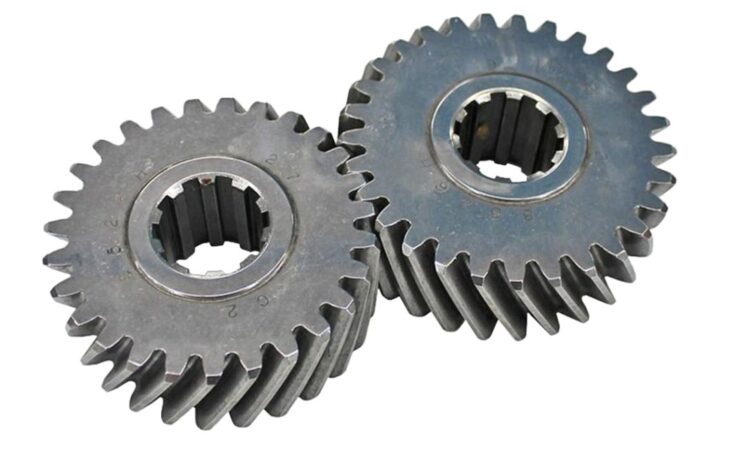
Before diving into the manufacturing process, it’s essential to understand the anatomy of a spur gear. Engineers cut teeth into a flat, disc-shaped wheel to create spur gears. The teeth of a gear evenly space themselves along its circumference and interlock with the teeth of another gear to transfer power between the two.
The pitch of a spur gear refers to the distance between the teeth and is an important consideration when designing a gear system. The gear center and axis are the points around which the gear rotates, and the bore and hub provide a way to attach the gear to a shaft or other component. The face and back of a gear refer to the opposite sides of the gear wheel.
Types of Spur Gears
There are three main types of spur gears: straight-cut gears, helical gears, and double helical gears.
- Straight-cut spur gears feature teeth that are cut straight across the face of the gear and are the most basic sort of spur gear.
- Helical gears feature inclined teeth cut diagonally across the gear face. Its design aids in the reduction of noise and vibration in the gear system.
- Double helical gears, also known as herringbone gears, feature teeth on both sides of the gear that are cut in opposite orientations. Its design aids in the elimination of axial thrust as well as the reduction of noise and vibration.
Benefits and Limitations of Spur Gears
Spur gears are simple, dependable, and simple to make, among other advantages. Additionally, their excellent efficiency and capacity for powerful power transmission have made them renowned. However, the amount of noise and vibration produced by spur gears may be a limitation. Particularly at high speeds, straight-cut gears can be rather noisy. Although producing helical and double helical gears is more complicated and expensive, they aim to reduce noise and vibration.
The Manufacturing Process of Spur Gears
There are several crucial processes in spur gear manufacturing. To prepare the gear blank, the manufacturer will cut a disc-shaped piece of metal into the gear shape, ensure the blank is cut to the proper diameter, and drill the center hole to construct the bore.
The gear blank will then have its teeth cut into it. Several methods, such as hobbing, shaping, and broaching, can be used for this purpose. The most widely used method is hobbing, which involves gradually removing the gear blank’s teeth with a specific cutting tool called a hob.
The gear is heat-treated to boost its strength and longevity after the teeth are cut. To enhance the gear’s aesthetic and functionality, surface polishing is also done. To remove any sharp edges or flaws; this may entail grinding, polishing, or other techniques.
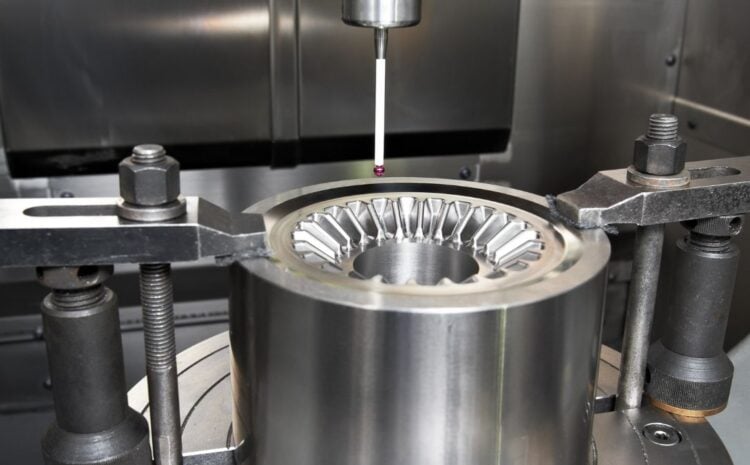
The equipment is then examined and tested to make sure it satisfies the necessary requirements. This may entail taking measurements of the gear’s size, inspecting it for flaws, and undertaking dynamic testing to gauge how well it performs under load.
Comparison with Other Gear Types
One type of gear seen in industrial and mechanical applications is spur gear. Helical gears, bevel gears, and worm gears are further frequent varieties of gears. In contrast, to spur gears, helical gears have inclined teeth that lessen noise and vibration. Worm gears are used to transmit power between perpendicular shafts, while bevel gears are used to transmit power between shafts that are at an angle to one another.
It’s critical to select the appropriate type of gear for a given application since every type has different advantages and disadvantages.
Applications of Spur Gears
Automobile transmissions, conveyors, and manufacturing equipment are just a few of the industrial uses for spur gears. They are also frequently discovered in home equipment like blenders and washing machines. Spur gears are frequently employed when substantial amounts of power need to be transferred between two parallel components.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Regular maintenance and repairs are necessary to preserve the efficiency and durability of spur gears. This may entail inspecting the gears for wear and damage, cleaning and lubricating them, and replacing any worn or broken components. If the gears are not properly maintained, they may get noisier and vibrate more, lose efficiency, and eventually stop working altogether.
Repair or replacement may be required if the gear fails. If the damaged gear cannot be repaired, it may need to be replaced. Repair may involve re-cutting or re-machining the damaged gear. Collaborating with a skilled specialist during gear system maintenance and repair is crucial to ensuring that the work is done correctly and safely.
Conclusion
Numerous industrial and mechanical applications utilize spur gears, which are a significant type of gear. They are a well-liked option for a variety of industries because of their famed simplicity, dependability, and ease of manufacture. The preparation of the gear blank, the cutting of the teeth, the heat-treating of the gear, as well as final product inspection and testing are all essential phases in the manufacturing of spur gears. Spur gears provide a number of advantages, but their level of noise and vibration can also be a drawback. To guarantee that spur gears continue to function at their peak over time, routine maintenance and repair are necessary.