As technology has advanced, so too has the way we create gears for various industrial applications. One such process is gear hobbing, a technique that allows for the creation of high-quality gears in a cost-effective and efficient manner. In this article, we’ll explore the hobbing process in detail, discussing its advantages, applications, and common challenges.
What is Hobbing?
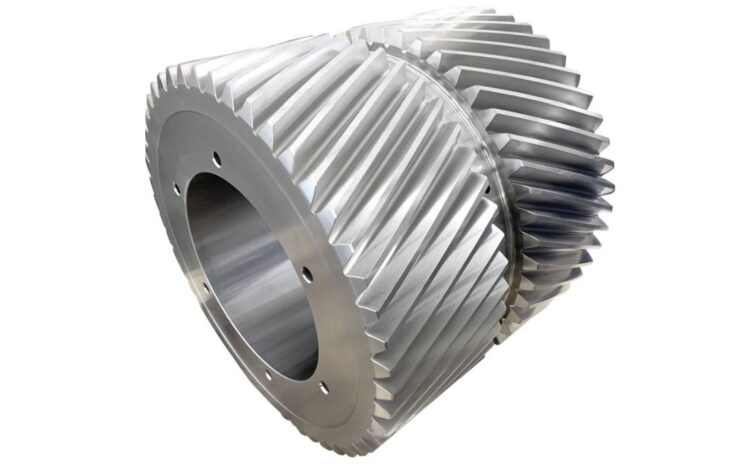
Hobbing is a gear manufacturing process that uses a specialized tool known as a hob to create gears of different sizes and shapes. A hob is a cutting tool with helical teeth that resemble the teeth of the gear it is intended to produce. It is rotated at a high speed while being fed into a blank workpiece, thus cutting the teeth into the workpiece. This process is repeated for each tooth until the desired gear is produced.
The Hobbing Process
The hobbing process is a multi-step operation that involves several specialized machines and tools. Here are the steps involved:
- Design and Preparation: The first step in hobbing is to design the gear that needs to be produced. This involves using computer-aided design (CAD) software to create a 3D model of the gear. Once the design is complete, a blank workpiece is chosen, typically made of steel or other strong metals.
- Mounting the Workpiece: The workpiece is mounted on a spindle, which is usually connected to a motor that rotates the workpiece at a high speed. The spindle is placed in the hobbing machine, which also contains the hob that will be used to cut the teeth.
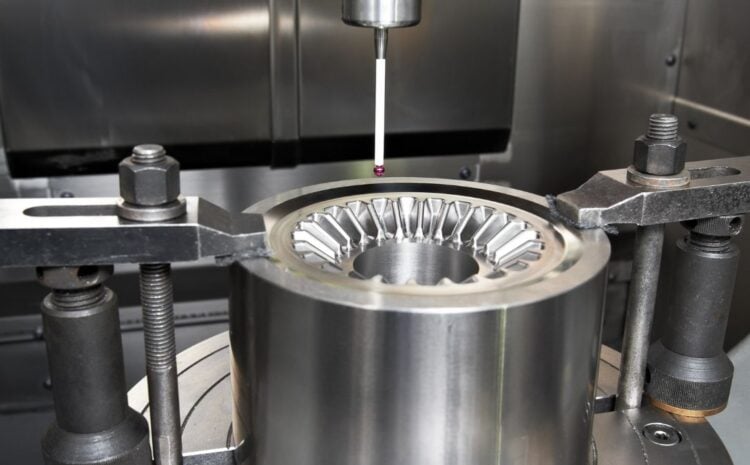
- Feeding the Hob: The hob is fed into the workpiece at a precise angle and speed, cutting the teeth into the workpiece. The cutting speed and angle must be carefully controlled to ensure a consistent and accurate cut.
- Finishing: Once the teeth have been cut, the gear is ready for finishing. This involves using specialized tools to remove any rough edges or burrs and to ensure that the gear is of the correct size and shape.
Advantages of Hobbing
One of the biggest advantages of hobbing is its efficiency. It is a highly automated process that requires very little manual labor, which makes it faster and less expensive than other gear manufacturing methods. Additionally, the hobbing process allows for the creation of gears with a high degree of accuracy and precision. This makes it ideal for applications where tight tolerances are required.
Another advantage of hobbing is that it can be used to produce a wide range of gear types, including spur gears, helical gears, and worm gears. This versatility makes hobbing an attractive option for manufacturers across a variety of industries.
Applications of Hobbing
Hobbing is used in a wide range of applications across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. It is commonly used to produce gears that are used in engines, transmissions, and other mechanical systems.
Spur gears are the most commonly produced gear type using hobbing. They are typically used in applications where the gears need to transmit power between two parallel shafts. Helical gears, on the other hand, are used in applications where the gears need to transmit power between non-parallel shafts. Worm gears are used in applications where high gear reduction is required.
Hobbing Tools and Materials
The tools used in hobbing must be made of high-quality materials to ensure that they are durable and long-lasting. Typically, hobs are made of high-speed steel or carbide. The workpieces, meanwhile, are typically made of steel or other strong metals that can withstand the cutting process.
Choosing the right tools and materials is essential for a successful hobbing process. The hob must be properly matched to the gear it is intended to produce, with the right number of teeth and tooth profile. The workpiece must also be carefully selected to ensure that it is the correct size and shape.
Common Challenges in Hobbing
While hobbing is an efficient and accurate method of gear production, there are some common challenges that manufacturers may encounter. One such challenge is tool wear. Over time, the cutting edges of the hob can become dull, resulting in lower-quality gear. To combat this, manufacturers must carefully monitor the tool and replace it when necessary.
Another common challenge is chatter, which is a vibration that can occur during the cutting process. Chatter can result in an uneven surface finish and can even damage the hob or workpiece. To prevent chatter, manufacturers must carefully control the cutting speed, angle, and other parameters.
Conclusion
Hobbing is a versatile and efficient method of gear manufacturing that has become increasingly popular in recent years. It allows for the production of high-quality gears in a cost-effective and automated manner. By carefully selecting the right tools and materials and closely monitoring the process, manufacturers can create gears that meet the tight tolerances required in today’s industrial applications.
In summary, hobbing is an excellent option for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality gear in a cost-effective and efficient manner. With the right tools and materials, and careful attention to the hobbing process, manufacturers can create gears that meet the precise specifications required for various industrial applications. Whether you are in the automotive, aerospace, or industrial machinery industry, hobbing is a process that can help you meet your gear manufacturing needs.