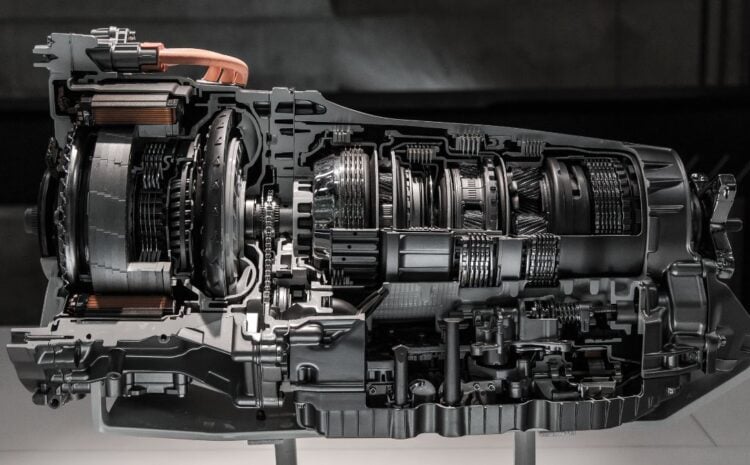
One of the most fundamental mechanical parts, gears are crucial for transferring motion and power in a variety of systems. These gears find applications in a wide range of products, including toys, musical instruments, home appliances, and industrial gear. This article will cover the various gear types, their advantages and disadvantages, as well as their applications in manufacturing and other industries.
Types of Gears
Let’s look at the various sorts of gears available before delving into gear uses. To choose the best gear for a given application, it is essential to comprehend the many types of gears and their features. Below are the most typical types of gears:
Spur Gears: To transmit motion and power, spur gears, which have cylindrical gears and straight teeth, mesh with one another. Spur gears are the simplest and most frequently used type of gears, finding applications in a variety of settings, such as power equipment, printing presses, and automobile transmissions.
Helical gears operate more smoothly and quietly than spur gears because they feature inclined teeth that gradually mesh. These gears find frequent applications in pumps, power tools, and vehicle transmissions.
Bevel gears transfer power between non-parallel shafts and have teeth cut on a cone-shaped surface. They find frequent applications in agricultural equipment, automobile differentials, and hand drills.
Worm Gears: Worm gears transmit motion and power by the meshing of a helical gear and a screw gear. Elevators, conveyor systems, and industrial machines all frequently employ them.
A central sun gear, one or more planet gears, and an outer ring gear make up planetary gears. These gears find applications in industrial machinery, robotics, and automatic transmissions.
Rack and pinion gears transform rotational motion into linear motion and find applications in steering systems, elevators, and CNC machines.
Uses of Gears in Manufacturing
There are many uses for gears in manufacturing, where they convey motion and power in a variety of industrial machinery and equipment. Following are a few of the most typical uses for gears in the manufacturing industry:
Gear trains transfer power and motion between rotating shafts in various forms of machinery, such as lathes, milling machines, and drills. By altering the gear ratio, they enable the operator to change the machine’s speed and torque.
Conveyor Systems: In automated material handling equipment, such as assembly lines, warehouses, and distribution centers, conveyor systems use gears to transmit power and motion. They enable the smooth and effective transportation of resources and objects.
Gears are a crucial part of robotics and automated machines because they allow for exact control of motion and speed. These gears find applications in packing equipment, manufacturing lines, and other forms of industrial automation.
Heavy Equipment: In order to transfer power and motion from the engine to the wheels or tracks, gears are employed in heavy equipment including bulldozers, excavators, and cranes. They offer the torque and power required to carry out heavy-duty activities.
Industrial printing: Printing presses use gears to move ink to paper, enabling high-volume, high-speed printing. In offset, flexographic, and digital printing, they are employed.
Uses in Aerospace: Gears are employed in many aerospace applications, including control systems, landing gear systems, and jet engines. They supply the required propulsion and management to keep spaceships and aircraft moving.
Advantages of using gears in manufacturing
The following are some benefits of employing gears in manufacturing:
- High efficiency: The transmission of power and motion by gears can be done so well that minimal waste and energy are produced.
- Control and precision: Gears enable exact motion and speed regulation, which is critical in many industrial applications.
- Longevity: Gears can survive for many years with proper maintenance and are frequently composed of sturdy materials like steel or cast iron.
- Versatility: Gears can be employed in a wide range of applications, from light industrial machinery to small household products.
- Cost-effectiveness: As compared to other means of transferring force and motion, like hydraulics or pneumatics, gears are frequently more affordable.
Disadvantages of using gears in manufacturing
Although gears provide many benefits, there are certain drawbacks to employing them in manufacturing, such as:
- Noise and vibration: When used in specific applications, such as medical equipment or precision instruments, noise and vibration produced by gears might be problematic.
- Wear and tear: Gears can lose efficiency and shorten their lifespan as a result of wear and tear over time.
- Gear lubrication: is necessary for smooth operation, which might increase equipment operating and maintenance expenses.
- Complexity: In order to assure optimal functioning, gears must be carefully designed and manufactured.
Conclusion
In many industrial applications, gears are a crucial component because they allow for the exact and effective transmission of motion and power. To choose the best gear for a given application, it is essential to understand the various gear types and their uses. While gears have many benefits, there are a few drawbacks to take into account when creating and utilizing gear systems. In spite of this, gears will always be essential to the industrial sector and other sectors, enabling the effective and dependable operation of machinery and equipment.